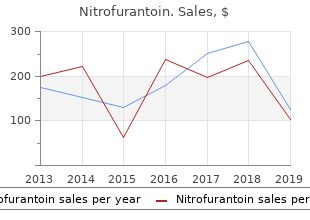
Nitrofurantoin
"Cheap nitrofurantoin 50mg with amex, antibiotics for dogs simplicef."
By: Karen Patton Alexander, MD
- Professor of Medicine
- Member in the Duke Clinical Research Institute

https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/karen-patton-alexander-md
Other areas of regenerative medicine research in Investigator Prize by the American Society for Virology progress include intestinal and tracheal replacement discount nitrofurantoin generic virus model. Finally purchase nitrofurantoin 50 mg free shipping antibiotics vitamin k, The center welcomed Chris Walker buy nitrofurantoin 50mg line antimicrobial light, PhD we are targeting 2020 to start the second phase of our its newest faculty member this year. Often, symptoms can be treated with success, but the 2019 Jun;38(6S Suppl 1):S14-S19. Vaccination to Prevent T Cell Subversion Can Protect Against Persistent Hepacivirus a team of center investigators (Mejias, Ramilo, Peeples) Infection. Tissue Eng Residues in the Apical Loop of the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Protein F2 Subunit at Nationwide Children�s established the Center for of airway disease. Feng who studies hepatitis virus infection regeneration and to develop next-generation reparative solutions. The institute combines robust clinical diagnostics, leading-edge research and development, and Christian L. Lauber, PhD example of the virtuous cycle of discovery leading to high-performance computing to enable precision genomic medicine. Barrie, PhD Executive Director Senior Director discoveries around autism and psychiatric genetics of Cecelia R. Since early 2017, the institute has performed clinical exome sequencing to identify alterations in the protein-coding regions In 2018, the Steve and Cindy Rasmussen Institute for (�exons�) of all human genes. Magrini, PhD Genomic Medicine launched a comprehensive protocol a genetic diagnosis for greater than one-third of families. Co-Executive Director Senior Director studying the genomes of children with cancer and For patients in whom this test does not reveal a diagnostic hematologic disease. With a focus on rare, relapsed answer, enrollment in the institute�s Rare Disease or treatment-refractory cancers, we can identify new Genomics Study examines the genome more broadly for treatment options, potentially leading to improved genetic clues underlying their disease. To date, we have The Big Data nature of genome-based clinical tests and studied more than 100 pediatric cancer patients on this research studies requires state-of-the-art cloud computing protocol. We are advancing the understanding of the molecular underpinnings of genetic disease through the development of novel computational tools and the application of big data technologies. By combining novel laboratory methods, state-of-the-art bioinformatics solutions and machine learning technologies, we are driven to create a future where no child with genetic disease goes undiagnosed and every child with cancer receives optimal treatment based upon their genomic profle. Expanding the Clinical History Associated with Syndromic Klippel-Feil: A Unique Case of Comorbidity with Medulloblastoma. You can also access practice tools, referral information and training opportunities � including residencies and fellowships � at NationwideChildrens. Aaron West Elena Chiappinelli Janel Hancock Emily Loughley Donna O�Connor Sara Styer Krista Wheeler Beth Deley Linda Humston Angela Lyons Maria Penrose Karen Sweitzer Gail White Isha Dhamija Cindy Jenkins Lindsay Maggs Charlotte Prewitt Laura Taylor Susannah Wolman Jonathan Dowdell Katie Johnson Bethany Malloy Amy Randall-McSorley Alexis Tindall Julie Zaremski Kim Dwyer Laura Kelley Nicole McClendon Megan Rhodes Jordanna Tomblin Rachel Zbiegien Robin Egan Ashley Kiel Susan Meyer Teaya Rough Kristin Tomlinson Paige Zilincik To request additional copies of this report, call (614) 355-0485. The College also reserves the same right as to any other material in this catalog. This version of the catalog for Palmer College of Chiropractic can be found on our website: As changes occur, the most up-to-date information can be found on our website: As you read through this catalog, you�ll discover a great deal about the founding institution of chiropractic, our campuses and the exciting career that awaits you as a future Palmer graduate. The College clinic system delivers 170, 000 patien visits every year, and Palmer is home to the largest chiropractic research center in the U. Whichever campus you select, you�ll have access to some of the most advanced technology in classrooms and health centers. Additionally, the Palmer Center for Business Development offers free learning modules, online resources and a professional network dedicated to promoting business skills and entrepreneurship among our students and alumni. All of this adds up to greater access to information and more opportunities for skill development, which give Palmer graduates greater opportunities for success in the profession. When you graduate, you�ll join a distinguished group of more than 30, 000 Palmer alumni, who comprise one-third of all chiropractors in the world and help millions of patients worldwide.
Approximately 80% of all cervical spine injuries affect the lower cervical spine and these injuries Eighty percent of all cervical are often associated with neurological deficits [17 cheap 50mg nitrofurantoin with amex antibiotics for uti sepsis, 22 purchase nitrofurantoin overnight delivery infection white blood cells, 32 order 50mg nitrofurantoin free shipping treating uti quickly, 182]. The variety and injuries affect the subaxial heterogeneity of subaxial cervical spinal injuries require accurate characteriza spine tion of the mechanism and types of injury to enable a comparison of the efficacy of operative and non-operative treatment strategies. Frequency of neurological deficits in subaxial injuries Types and groups Number of patients Neurological deficit Type A 66 42. Treatment with traction conservatively and prolonged bedrest has been associated with increased morbidity and mor tality and has widely been abandoned today. After reduction of dislocated frac tures, more rigid fixation techniques (halo vest fixation, Minerva cast) appear to have better success rates than less rigid orthoses (collars, traction only). Surgical indications for subaxial injuries irreducible spinal cord compression vertebral subluxation of 20% or more ligamentous injury with facet instability failure to achieve anatomical reduction (irreducible injury) spinal kyphotic deformity more than 15� persistent instability with failure to maintain reduction vertebral body fracture compression of ligamentous injury with facet instability 40% or more Most subaxial spine injuries Both posterior (Fig. The screw is directed from the medial upper quadrant of the facet joint 20�25� laterally and 30�40� cranially. Failures of this technique which may result in reoperations are rare (0�6%) [119, 133]. Standards Standards of care cannot of care or widely accepted guidelines could not be derived from the literature derived from the scientific [11]. In view of the lack of scientific evidence, the authors feel that a pragmatic literature approach related to the fracture types is reasonable. However, we want to acknowledge that this approach is anecdotal but appears to provide a satisfactory outcomeinalargetraumareferralcenter. Deformities of 15��20� or more should be considered for operative stabilization with anterior cervical fusion [11, 12, 14]. Therefore, we prefer a corpectomy and reconstruc tion of the anterior column with a tricortical bone graft and plate fixation (Fig. Therefore, we prefer an operative treatment (anterior or poste require operative treatment rior instrumented fusion) because it shortens the treatment duration. Standard lateral (a) and anteroposterior (b) radiographs demon strated a malalignment of C5/C6, indicating a flexion injury at this level. Complications Overall, 5% of patients with compressive injuries of the subaxial cervical spine had persistent instability after non-operative treatment. In contrast, nearly every patient treated with anterior (100%, 22 of 22 patients) or posterior (96%, 26 of 27 patients) fusion procedures developed a solid fusion [14, 22, 71]. Kyphosis or subluxation develops in about 10% of patients who are treated with posterior fusion[38, 71]. Cervical spine injuries account for definition of spinal instability remains enigmatic. Late whiplash syndrome re score of less than 9 are at highest risk of concomi sembles the feature of a chronic pain syndrome. Functionally, the cervical spine tients with cervical strains/sprains due to rear-end is divided into the upper cervical spine [occiput collision. Oblique views are safer and often more in 872 Section Fractures formative than swimmer views for the assessment ral canal and subsequently damage the spinal cord. Neu tures are comminuted fractures of the base and are rophysiological assessments are indicative of the associated with severe instability. In fractures of the axis body, external immobilization is suggested as the initial Specific treatment. Stable cal spine fractures can be classified into Type A atlas fractures can be treated conservatively while (compression), Type B (distraction) and Type C unstable atlas fracture. Atlantoaxial instabilities are relatively com with rigid external or internal fixation. Stable undis mon in patients with rheumatoid arthritis but rela placed Type A injuries of the lower cervical spine tively rare after trauma. Indi Cervical Spine Injuries Chapter 30 873 cations for surgical treatment for lower cervical achieve anatomical reduction (irreducible injury), spine injuries include irreducible spinal cord com persistent instability with failure to maintain reduc pression, ligamentous injury with facet instability, tion, and ligamentous injury with facet instability. Anterior fusion should not vertebral subluxation of 20% or more, failure to be performed without plate fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res:244�57 the author analyzes the results of 100 cervical spinal injuries that were treated opera tively and demonstrates that immediate reduction of the injury is more important for the further neurological outcome than improved surgical techniques.
50mg nitrofurantoin with mastercard. Synthetic Yarn Manufacturing Process - wet method.
In general purchase cheap nitrofurantoin on line antibiotic h49, the greater the neuromuscular involvement generic nitrofurantoin 50 mg overnight delivery virus free games, the greater the likelihood of having a spinal deformity and the greater the deformity will be generic 50mg nitrofurantoin overnight delivery infection prevention society. Pathogenesis the pathophysiology of neurogenic spinal deformities remains unclear. It seems logical to assume that the �collapsing kyphoscoliosis� is secondary to muscle weakness and yet the same deformity is seen in patients with spasticity. Classification the classic patient we think of having neuromuscular scoliosis has either cerebral palsy (upper motor neuron lesions) or Duchenne muscular dystrophy (peripheral muscular disease) [4]. These two etiologies are representative of the two main types of neuromuscular scoliosis. Classification of neuromuscular scoliosis Neuropathic conditions Myopathic conditions Upper motor neuron Muscular dystrophy cerebral palsy Duchenne and Becker syringomyelia limb girdle spinal cord injury facioscapulohumeral myotonic dystrophy Lower motor neuron poliomyelitis Arthrogryposis spinal muscular atrophy Congenital myopathies Mixed upper and lower motor neuron nemaline myelodysplasia (spina bifida) central core disease spinal trauma Spinocerebellar dysfunction Friedreich�s ataxia Hereditary motor sensory neuropathy Charcot-Marie-Tooth Lonstein et al. Neuromuscular curve classification Group I: double thoracic and lumbar curves, little pelvic obliquity, patient in balance. A thorough history should include: perinatal history development history family history A family history is required to assess the risk of a known etiology for the patient�s spinal deformity. Patients must be examined for both defor mities in the sitting and supine positions, giving us an immediate insight into the overall rigidity of both deformities. Of note, hyperlordosis can also be seen in neuromuscular scoliosis, leading to inability to sit properly. Sagittal imbalance the combination of pelvic obliquity and scoliosis tends to lead to spinal with apical kyphosis imbalance, resulting in abnormal pressure points. Clinical clues to neuromuscular scoliosis d a Eleven-year-old boy, idiopathic-like curve pattern, asymptomatic. His brother had undergone a selective thoracic posterior spinal fusion with Harrington rod 15 years earlier (c). A detailed examination of the hips particularly looking for hip contracture is crucial as they influence sitting balance and in par ticular can induce pelvic obliquity (Case Study 1). If pelvic obliquity is present, one should assess whether its origin is: suprapelvic intrapelvic infrapelvic [13] Pelvic obliquity Suprapelvic obliquity is secondary to the spinal deformity itself. Dubousset saw the pelvis as the 6th lumbar ver for neuromuscular scoliosis tebra and the pelvis being a simple extension of the scoliotic deformity resulting in pelvic obliquity. These may induce fixed or flexible sagittal spi nal deformity in the form of lumbar hyperlordosis. Orientation of the pelvis and lumbar lordosis needs to be assessed as an anteverted pelvis or compensatory hyperlordosis can indicate severe hip flexion contracture. These postoperatively maybecomemuchmoreapparentasthepatientsarenolongerabletocompen sate with their flexible lumbar spine. To differentiate between supra and infrapelvic obliquity, the patient is placed prone at the end of an examining table with the hips flexed over the edge of the table (negating the flexion hip contractures). Certain determines the extent patients (myelodysplasia) need a mobile lumbosacral junction to ambulate as of instrumented fusion they rely on pelvic thrust to propel their lower extremities to ambulate. Even in the wheelchair-bound patient, a mobile lumbosacral junction may be needed to perform self-catheterization. Neuromuscular Scoliosis Chapter 24 673 Neurological Examination the treating surgeon must complete a thorough physical examination not limited Always check abdominal to the musculoskeletal examination. Having the patient walk and run while looking for gait pattern and upper extremity posturing can elucidate a subtle spastic diplegia. A detailed neurological examination must be carried out to assess for both sensory and motor deficits. Testing reflexes and looking for long tract signs such as Babinski�s and Hoffman�s signs, clonus, and spasticity are all part of a first visit examination of a newly diagnosed scoliosis. If the child is unable to do so or uses their hands to push themselves up by adapting a wide base gait and locks the knees in extension with the hands and uses the hands to push themselves along on their legs, then this is considered a positive Gower test. Romberg�s test should also be performed to test cerebellar function (testing balance with eyes closed, feet side bysideandarmforwardflexed). Signsofcalfhypotrophyarealsodocumentedas a diagnosis of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease can be made.
Note: Diagnostic Criteria Acetazolamide is a sulphur containing medicine nitrofurantoin 50 mg on-line antibiotics for sinus infections in adults, do not use in patients allergic Patients presents with acute sudden onset of painful red eye in the affected to cheap nitrofurantoin amex virus hiv sulphur generic nitrofurantoin 50 mg free shipping antibiotic with milk. Hence, all There is usually dramatic visual impairment and vomiting may be present patients with Angle Closure Glaucoma should be referred to eye specialist. Standard Treatment GuidelinesStandard Treatment Guidelines 189189 Diagnostic Criteria Poor vision in the affected eye associated with High intraocular pressure Optic nerve damage New vessels on the iris if the cause is retinal diseases Pharmacological Treatment Management of these patients depends on the cause but it includes medical, surgical and laser. Referral Refer all patients suspected to have secondary glaucoma to a qualified eye specialist available at the Regional, Zonal or National Hospital. There is a chronic inflammation of the conjunctiva leading to scarring of the upper eyelid tarsal plate, entropion and in turn of eyelashes. Diagnostic Criteria Patients presents with photophobia in early stages or re-infection Follicles in the upper tarsal plate seen as round and white nodules in active diagnostic. Weight (kg) I-day regimen < 15 20mg/kg once daily Treatment of the preexisting eye disease is highly recommended. Note: Preventive chemotherapy in mass treatment campaign is conducted only once a 14. Diagnostic Criteria Patients presents with photophobia in early stages or re-infection 14. Re-assess on 3 monthly basis if there are signs of disease progression, restart treatment if any, with close follow up. Give Antioxidant in non-proliretative Diabetic Retinopathy Surgical Treatment C: Multivitamin + Beta-carotenoids, Zinc Sulphate and Lutein, 1 tablet once this is done in the proliferative stage daily to a maximum of 3 months It involves removal of vitreous and or blood, peeling of formed fibrovascular tissue and reattachment of retina if the retina is detached Surgical Treatment It is combined with retinal photocoagulation Type of surgery depends on the presentation/ stage of the disease the vitreous cavity may be filled with temponade liquid such as silicon oil or expansile gas like sulfur perfluoropropane or hexafluoride depending 14. There are mainly 4 types of refractive errors namely presbyopia, myopia, mentioned above astigmatism and hyperopia. Attendance to heath facility is also a Poorly controlled diabetes and diabetic retinopathy can lead to blindness good opportunity for screening of glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy All patients with diabetes mellitus regardless of their eye conditions, should have a thorough eye examination by available eye care personnel or an eye Non-Pharmacological Treatment specialist at least once a year. Convex lens spectacles for near vision Dilated eye examination and direct viewing of the retina by an Standard Treatment GuidelinesStandard Treatment Guidelines 193193 14. Diagnostic Criteria It is common in young age between 5�25 years the condition persists throughout life If not treated early, it may progress rapidly and lead to retinal complications It is diagnosed through refraction. Diagnostic Criteria Ocular strain Diagnosis in children should be reached after refraction through a pupil that is dilated Non-Pharmacological Treatment Convex lens spectacles for constant wear Note: Spectacles should be given to: Children who have only significant hypermetropia (more than +3. Diagnostic Criteria Poor vision at distance, Photophobia Headache (sometimes). They have visual impairment even with treatment and or standard refractive correction and 194 Standard Treatment Guidelines 14. Inability to Recognizing people in the streets, Diagnostic Criteria Reading black boards, It is common in young age between 5�25 years Writing at the same speed as peers and the condition persists throughout life Playing with friends. Investigations Non-Pharmacological Treatment Assessment of these patients is by thorough eye examination to determine Concave lens spectacles for constant wear. It is less Non-Pharmacological Treatment manifested in children as they have a high accommodative power. Disease Visual Affected Cornea Pupil Pain Discharge Condition Acuity Eye Diagnostic Criteria Allergic/ viral Good Both Clear Normal No Watery/mucoid Poor vision at distance, Conjunctivitis Photophobia Bacterial Good Both Clear Normal No Purulent Headache (sometimes). Conjunctivitis Diagnosis is reached through refraction Ophthalmia Poor +/ One/both Cloudy Normal Yes Copious neonatorum +/ +/ purulent Non-Pharmacological Treatment Cornea ulcer Poor One/ Gray Normal Yes Watery/purulent Cylindrical lenses spectacles for constant wear. They have visual impairment Acute Poor One Cloudy Mid Yes Watery even with treatment and or standard refractive correction and glaucoma dilated Standard Treatment GuidelinesStandard Treatment Guidelines 195195 14. The management of these injuries is guided by history from the patient and ocular findings by the clinicians. Diagnostic Criteria Corneal abrasion/laceration with or without an imbedded foreign body. Investigations this is done after the first aid measures Test the visual acquity Examine the injured eye with slit lamp or magnifier including fluorescein staining to reveal foreign body or corneal laceration Non-Pharmacological Treatment Provide first aid measures to the patients as per presentation If no penetration, irrigate the eye with clean water or Ringers Lactate to reduce chemical substance in the eye Remove foreign body if visible with a cotton bud or surgical blade if shallow. Pharmacological Treatment At the primary care: Corneal Abrasion: A: Chloramphenical eye ointment 1%, 8 hourly to the injured eye until no fluorescein staining Steps Guiding Management of Complicated Blunt Trauma Complicated blunt trauma is a trauma where the vision is poor, patinets experiences pain and there is hyphaema.
References:
- https://www.hanc.info/cp/Documents/PPTSlidesInstructorNotes102209.pdf
- https://www.div52.net/images/PDF/D52-IPB/IPB_2012-16-1-WINTER.pdf
- https://www.lmunet.edu/academics/catalogs/graduate/2018%202019%20Graduate%20Catalog%20Vol%202%20D1.pdf
- https://history.nasa.gov/SP-4407vol7.pdf