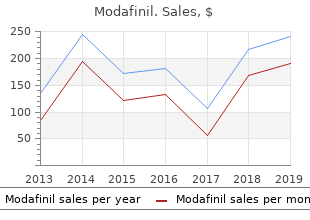
Modafinil
"Modafinil 100mg with visa, insomnia 15 weeks pregnant."
By: Joshua Apte PhD
- Assistant Professor
- Environmental Health Sciences

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/joshua-apte/
It is therefore important to be aware of macular * degeneration purchase genuine modafinil line insomnia and icd-9, the leading cause of blindness and severe vision loss in Australia modafinil 100mg line insomnia 420. This booklet is designed to provide general information about macular degeneration generic 100 mg modafinil free shipping insomnia headaches. It explains all about macular degeneration, how it affects vision and how to reduce risk. It also explains how to identify signs and symptoms of the disease as well as the treatment options and support services available. This publication is one of a series produced by Macular Disease Foundation Australia as part of the work undertaken in education and awareness to reduce the incidence and impact of this disease in Australia. The front of the eye, comprising the cornea, iris, pupil and lens, focuses the image onto the retina, which lines the back of the eye. The retina is sensitive to light and acts like the flm in the camera, capturing images and then sending them via the optic nerve to the brain, where the images are interpreted. It is responsible for the ability to read, recognise faces, drive a car, see colours clearly and any other activity that requires fne vision. It is used to see general shapes and provides ‘get-about’ vision, which is also called side vision or peripheral vision. Macular degeneration is the name given to a group of chronic, degenerative retinal eye diseases that cause progressive loss of central vision, leaving the peripheral or side vision intact. Macular degeneration is usually related to ageing and most frequently affects people over 50 years of age. Macular degeneration is progressive and painless and although it can lead to legal blindness, it does not result in total or ‘black’ blindness. About one in seven Australians (1 million people) over the age of 50 has some evidence of macular degeneration. Approximately 17% of these people (170, 000 Australians) experience vision impairment. It is the leading cause of legal blindness in Australia and is responsible for 50% of all cases of blindness. An optometrist or an eye specialist can examine the eyes for the early signs of the disease (drusen) by looking inside the back of the eye using special optometric equipment. However, the existence of drusen does increase the chance of developing late stage macular degeneration. Some people who have either the early or the dry form can later develop the more aggressive wet form. It is therefore important for any sudden changes in vision to be reported to the eye specialist as a matter of urgency. Choroid This is the most severe form of the disease with approximately 21, 000 new cases diagnosed annually in Rapidly growing vessels break Australia. The Amsler grid is an essential tool to self-monitor for possible symptoms or sudden changes in vision. One in seven Australians over the age of 50 has some evidence of the disease, and the incidence increases with age. It can also be hereditary, with a 50% chance of developing it if there is a direct family history. Since at least 70% of cases have a genetic link, it is critical that people with macular degeneration inform their siblings and children, and encourage them to have their eyes tested and macula checked. Studies have shown that those who smoke are three to four times more likely to develop macular degeneration, and smokers may also develop the disease fve to ten years earlier than non-smokers. Those with a specifc genetic predisposition who smoke have a signifcantly increased risk of developing wet macular degeneration. Nutrition for eye health Studies show that diet is important in reducing the risk of macular degeneration and in slowing its progression. Eating a healthy, well- balanced diet high in antioxidants, vitamins and other nutrients can help keep our eyes healthy. These are present in high concentrations in a healthy macula and help to protect the eye. They are found in dark green leafy vegetables such as spinach and silver beet as well as naturally yellow fruit and vegetables such as sweet corn and capsicum. In addition, vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc and selenium are important antioxidants for a healthy macula.
The current evidence order modafinil 200mg on-line sleep aid for dogs, a possible invasive fungal infection purchase modafinil with mastercard insomnia 55, then antifungal therapy that reviewed below purchase modafinil 200 mg with visa insomnia psychology, suggests that evolving diagnostic methods may covers a broader range of fungal pathogens, including molds, lead to better targeting of those febrile patients in need of pre- should be quickly applied using one of the broad-spectrum emptive antifungal therapy as an alternative to broad use of antifungals that has documented efficacy in the empirical set- empirical antifungals [213]. Another important unresolved question is use of the antifungals among 41 neutropenic patients who would other- preemptive antifungal approach in patients who are already wise have qualified for empirical antifungal treatment on the receiving anti-mold prophylaxis [242]. When Should Antifungal Prophylaxis be Given and With has also proven to be as effective as fluconazole or itraconazole What Agents? Fluconazole, need for parenteral administration are limitations of these itraconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole, micafungin, and agents. It should be emphasized that fluconazole will not pro- caspofungin are all acceptable alternatives. The toxicity of amphotericin B desoxycholate makes it posaconazole should be considered for selected patients >13 less desirable for prophylactic use, despite its very broad anti- years of age who are undergoing intensive chemotherapy for fungal activity. Prophylaxis against Aspergillus infection in pre- aconazole is a reasonable recommendation for Candida pro- engraftment allogeneic or autologous transplant recipients phylaxis in the high risk group [193, 201]. Accordingly, there is reason to limit fewer Aspergillus infections and improved survival but with fluconazole prophylaxis to only those patients who are at sub- more-serious adverse events, compared with a heterogeneous stantial risk for invasive infection. The threshold incidence of control group heavily weighted by fluconazole recipients [201]. Candida infection at which fluconazole prophylaxis appears to Posaconazole is currently available only in an oral formulation, be efficacious is 6%–10% in controlled studies and in meta- and its oral absorption is highly dependent upon concomitant analyses of prophylaxis [245–247]. Its bio- Candida infection rates at this level are usually seen among availability is variable and unreliable if not taken in conjunction high-risk patients with cancer who are not receiving prophylaxis. Among lower-risk patient populations, with vinca alkaloids or high doses of cyclophosphamide and invasive candidiasis is rare [245] and generally does not merit anthracyclines should be avoided until these interactions have routine fluconazole prophylaxis. Although routine azole drug level oral solution doses of 200 mg twice a day; however, the oral monitoring during prophylaxis is not recommended, low solution is rarely employed because of poor tolerability levels of the oral mold-active azoles have been noted [260, [249, 255]. Therefore, drug level monitoring may aid in deci- some centers, no large randomized studies involving patients sions about dosing in some patients. Prophylaxis stop-dates for patients 2 distinct periods of risk for invasive mold infections: the first with acute leukemia generally coincide with myeloid re- during the neutropenic pre-engraftment phase and the second constitution. The focus of this guideline is the initial who continue antifungal prophylaxis long after engraftment, for risk period during neutropenia. What Is the Role of Antiviral Prophylaxis and What Virus fluconazole lacks anti-mold coverage; its prophylactic efficacy in Infections Require Antiviral Treatment? Respiratory virus testing (including testing for influenza, intensive galactomannan screening monitoring program [251]. Influenza virus infection should be treated with among those who received voriconazole but comparable survival neuraminidase inhibitors if the infecting strain is susceptible at 100 and 180 days. In the setting of an influenza exposure or outbreak, events associated with itraconazole but more adverse visual and neutropenic patients presenting with influenza-like illness hepatic events associated with voriconazole [252]. Prophylaxis (eg, oseltamivir and zanamivir) should be initiated while test should be given until recovery of the white blood cell count or results are pending. In the setting of an influenza outbreak, resolution of mucositis, whichever occurs later. Duration of aggressive infection control measures should be instituted to halt prophylaxis can be extended for persons with frequent recurrent further nosocomial spread [283]. Some experts believe that the management of other febrile neutropenic patients with documented influenza virus infection should be treated even cancer. Similarly, there is no clear reactivation of either virus; thus, prevention strategies for these 2 evidence from randomized trials that aerosolized or oral riba- herpes viruses are not discussed in this document [274]. There is no chemotherapy cycles or are within 6 months after the end of proven effective therapy for adenovirus infection, although therapy. However, family members of patients with cancer may some experts would employ cidofovir or ribavirin for clinically receive the live attenuated influenza vaccination. Authoritative evidence-based guidelines by examination of nasopharyngeal swab or washing specimens. Neutropenic patients infected with these respiratory vi- usually appropriate [292–294]. Although days of blood cultures performed on specimens drawn simultaneously neutropenia, duration of fever, and length of hospital stay have through the catheter and peripheral vein.
Effective modafinil 200mg. Prescription sleep aid Ambien is newest date rape drug.
Patients of precursor B immunophenotype receive standard Regimen B post induction therapy modafinil 100 mg fast delivery sleep aid long-term. These patients are eligible for the factorial methotrexate and pulses randomisation (R2) within Regimen B order 200 mg modafinil with visa sleep aid over counter. Patients in this group receive a 3-drug (dexamethasone discount 200mg modafinil sleep aid uk, vincristine and asparaginase) induction (Regimen A induction). Patients in this group received a 4-drug (dexamethasone, vincristine, asparaginase and daunorubicin) induction (Regimen B Induction). Randomisation 1(R1) – Dexamethasone Randomisation 2 All patients are randomised to receive either standard (6mg/m /day orally for 28 days) or short 2 (10mg/m /day orally for a total of 14 days) dexamethasone for induction therapy (see Figure 1). Start therapy with 2 6mg/m /day dexamethasone and adjust total dose after randomisation (see Section 7. Randomisation must be performed no later than after 7 days of treatment, otherwise the patient is not eligible for entry into the trial. Down’s syndrome patients are eligible for the dexamethasone randomisation (R1) but are not eligible for the methotrexate and pulses randomisation (R2). These patients should receive consolidation as per the treatment arm previously assigned for induction (Regimen A or B). Also Down’s syndrome patients who have a slow early response on day 15 bone marrow should transfer to regimen C induction on day 15. Once the sample has been taken consideration should be given to starting the low dose holding chemotherapy as per week 15 of Regimen C consolidation. These patients continue therapy as per Regimen C and are eligible for the methotrexate and pulses randomisation (R2). The same modality of imaging should then be used to calculate the reduction in tumour volume at day 29. Post-induction therapy is stratified according to the day 29 assessment result as described below (see also Figure 4) Patients with <35% reduction in tumour volume are considered poor responders and are taken off protocol treatment. Their further therapy should be discussed with the Chief Investigator or Co- investigators. Patients with ≥ 35% reduction in tumour volume are considered good responders and those of T immunophenotype receive Regimen C and are eligible for the methotrexate and pulses randomisation (R2). Post-induction therapy is stratified according to the immunophenotype and day 29 scan result.. Routine ultrasound of the testis should not be performed to detect sub-clinical enlargement. Standard treatment for those patients who still have a clinically enlarged testis at week 8 is testicular radiotherapy. Testicular radiotherapy should be given during the first cycle of maintenance - guidelines can be found in Appendix 10. Please discuss the result with your cytogenetic laboratory and, if in any doubt, contact Professor Christine Harrison and/or Professor Anthony Moorman at the Cytogenetics Coordinating Centre (contact details can be found in Appendix 20). If uncertain please discuss result with your cytogenetics laboratory and, if in any doubt, contact Professor Christine Harrison and/or Professor Anthony Moorman at the Cytogenetics Coordinating Centre (contact details can be found in Appendix 20). Slides from diagnosis and day 29 must be sent to the Chief Investigator for review. Any patient with an M2 marrow and high risk cytogenetics should be discussed with the Chief Investigator or Co-investigators. After completion of therapy, remission status will be ascertained by annual questionnaire to treatment centres for a minimum of five years following completion of maintenance therapy. Written informed consent is required for all patients and a negative pregnancy test within 2 weeks prior to starting treatment for female patients of childbearing potential. Patients with this disease should be treated on a suitable protocol for this condition. Patients in whom written informed consent has not been obtained from parents and/or patients prior to randomisation 5. The following patients are excluded from the methotrexate and pulses randomisation: 1. Any patient with significant renal impairment defined as renal function outwith normal limits corrected for age, pleural effusions or ascites. It is recommended that these patients be allocated high dose methotrexate as interim maintenance (without asparaginase) and vincristine and dexamethasone pulses during continuation therapy. The following assessments and procedures should have been performed prior to registration.
Strongly consider referral to nephrology any patients with a creatinine greater than 1 buy generic modafinil canada insomnia event. Patients with a creatinine clearance of less than 30 mL/min should be referred to nephrology for discussions of future options and to enhance the ability to receive a future transplant cheap modafinil 200mg without prescription insomnia 75 mg. These patients also have signifcant enough renal impairment that they also beneft from more intensive nutritional interventions and proper management of anemia and bone disease (American Diabetes Association order modafinil 200mg amex insomnia order online, 2004b; Karter, 2002; Lewis, Return to Algorithm Return to Table of Contents www. All patients found to have neuropathy should see a foot care specialist for preventive measures aimed at reducing the incidence of diabetic foot complications. Comprehensive foot exam with risk assessment A foot exam should include assessment for the following risk factor for complications: • Loss of protective sensation. Patients with reduced or absent sensation with either of these tests should be educated about their risk and the need for proper foot care to prevent foot complications. See Appendix C, "Using a Semmes-Weinstein Monoflament to Screen the Diabetic Foot for Peripheral Sensory Neuropathy, " and Appendix D, "Using a Tuning Fork to Screen the Diabetic Foot for Peripheral Neuropathy. As many as 36% of patients with diabetes have lower-extremity peripheral arterial disease based on lower- extremity blood pressure readings. However, a typical history of intermittent claudication or an absent peripheral pulse is less commonly noted. Initial screening for peripheral arterial disease should include asking about claudication and assessment of pedal pulses. Peripheral vascular disease in combination with peripheral neuropathy places patients with diabetes at increased risk for non-traumatic amputations of the lower extremity. Peripheral vascular disease may be slowed by smoking cessation and treatment of hypertension and dyslipidemia. Aggressive daily foot care, inspection of the feet at every offce visit for diabetes mellitus, early treatment of foot infections, treatment of callus, use of moisturizing lotion and proper footwear may forestall problems, including amputation. Vascular surgery may also prevent amputation in some patients with established severe peripheral vascular disease (American Diabetes Association, 2003). Proper high-risk foot management is necessary to prevent ulceration and amputation. Consider referral of patients with claudication and/or absent pedal pulses to vascular surgery. Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease Treatment includes control of cardiovascular risk factors (hypertension, dyslipidemia and smoking cessation) and aspirin use. Consider referring patients with known coronary artery disease to cardiology and patients with known carotid disease to a specialist. Metformin may be used in stable congestive heart failure if renal function is normal. Special Considerations • Hepatitis B vaccine should be administered to unvaccinated adults with diabetes who are < 60 years of age. It may be administered to unvaccinated adults with diabetes who are ≥ 60 years of age. Consider repeating the immunization for those at risk of losing immunity after fve years including nephrotic syndrome, chronic renal disease and other immunocompromised states. This section provides resources, strategies and measurement for use in closing the gap between current clinical practice and the recommendations set forth in the guideline. The subdivisions of this section are: • Aims and Measures • Implementation Tools and Resources Copyright © 2014 by Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement 42 Diagnosis and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Adults Sixteenth Edition/July 2014 Aims and Measures Note: a multifactorial intervention targeting hyperglycemia and cardiovascular risk factors in individuals with diabetes is most effective. Both individual measures of diabetes care, as well as comprehensive measures of performance on broader sets of measures, are recommended. Therefore, the aims and measures listed here are selected carefully in the interests of patient safety. Percentage of patients with blood pressure most recent measurement less than 140/90 mmHg. Note about trial measure: This measure is intended for internal quality improvement use to measure prevalence of patients with type 2 diabetes whose glucose and cardiovascular factors are poorly controlled. Percentage of newly diagnosed patients who are advised about lifestyle modifcation and nutrition therapy within one year of diagnosis. Percentage of patients with blood pressure most recent measurement less than 140/90 mmHg.
References:
- http://www.aetna.com/healthcare-professionals/documents-forms/asam-criteria.pdf
- https://www.health.gov.au/sites/default/files/documents/2020/02/australian-health-sector-emergency-response-plan-for-novel-coronavirus-covid-19_2.pdf
- https://www.governor.ny.gov/sites/governor.ny.gov/files/atoms/files/NYForwardReopeningGuide.pdf
- http://www.jsums.edu/universitycommunications/files/2012/11/Jacksonian-without-indicia.pdf?x91926
- https://www.westga.edu/~distance/dla/pdf/2019-dla-proceedings.pdf