Rumalaya forte
"Rumalaya forte 30pills on-line, spasms meaning in telugu."
By: Joshua Apte PhD
- Assistant Professor
- Environmental Health Sciences

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/joshua-apte/
Psychiatric) More likely to order genuine rumalaya forte on-line spasms constipation be from psychiatric illness: Auditory and command hallucination Hallucinations and illusions incorporated into delusional system Age of onset 13–40 yr old Flat affect Normal orientation Disorganized attention the following groups are considered to cheap rumalaya forte 30pills with mastercard spasms right side of body be at higher risk for nonpsychiatric illness: Elderly History of substance abuse No pre-existing psychiatric history Presence of pre-existing medical disorders Lower socioeconomic level Visual hallucinations more common: Delirium Dementia Migraines Dopamine agonist therapy generic 30 pills rumalaya forte spasms treatment. Hallucinations from some intoxications such as methamphetamine or cannabis may persist even after drug is metabolized. Admission Criteria Medical condition requiring admission Acute psychiatric illness or decompensation of chronic psychiatric illness requiring psychiatric hospitalization Discharge Criteria Symptoms have resolved and reversible medical cause. Even though 10% of cases of schizophrenia occur in patients older than 45, do not assume hallucinations are from psychiatric cause in older age group without extensive workup. Do not treat hallucinations with excited delirium from an acute intoxication (except due to ethanol) with antipsychotic agents. Pediatric Considerations Suspected cases of child abuse or neglect require referral to child protective services. Use appropriate physical and chemical restraints to control violent and agitated patients to protect the patient and staff from physical injury. Do not assume once a violently agitated patient is calm that the patient is recovering. Clenched fist injuries involve a variety of pathogens, including anaerobic Streptococcus and Eikenella spp. Throbbing pain of the distal pulp space Vesicles containing nonpurulent fluid are present and may form bullae. Web space abscess: Pain and edema of the affected web space and adjacent palm Fingers are held abducted. Palmar space infections: Thenar space infection: Pain, tenderness, tense edema of thenar eminence Dorsal edema without tenderness Thumb is held abducted and flexed, and passive adduction is painful. Midpalmar space infection: Pain, edema, and tenderness of the midpalmar space Dorsal edema without tenderness Motion of middle and ring fingers is painful Hypothenar space infection: Pain and fullness over hypothenar eminence No limitation of finger movement History See Signs and Symptoms. Imaging Radiographs are usually not helpful unless there has been trauma or a suspected foreign body. With felon, flexor tenosynovitis, and palmar space infection, radiograph may identify osteomyelitis or foreign body. The differential for palmar space infection includes flexor tenosynovitis, cellulitis, and web space infection. If necessary, the lateral nail fold may be incised tangential to the curvature of the nail. When pus is present under the dorsal roof of the proximal nail, remove 1/3 of the proximal nail. Disruption of fibrous septa is no longer recommended: Results in an unstable fingertip Loculations may need to be broken up. Give oral antibiotics to cover skin pathogens, place a drain, and recheck in 48 hr: Cephalexin, dicloxacillin Herpetic whitlow: Usually self-limited; do not incise and drain. If there are no signs of infection and no joint penetration, patients may be considered for outpatient treatment with oral antibiotics after appropriate irrigation and wound care: Ampicillin/clavulanate or penicillin V + cephalexin or dicloxacillin Do not primarily close lacerations associated with a human bite; delayed primary closure or healing by secondary intention is appropriate. Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus hand infections in an urban setting. See Also (Topic, Algorithm, Electronic Media Element) Hand Infections emedicine. Pathophysiology: Acids cause coagulation necrosis with eschar, usually limiting penetration to deeper tissue. Alkalis cause liquefaction necrosis and soluble complexes that penetrate into deep tissues. Damage also occurs through oxidation, protein denaturation, cellular dehydration, local ischemia, and by metabolic competition/inhibition. The toxicity of the materials relates to the particular substances and their effects. Use Level A protective gear if safety not established Anyone able to walk and talk is minimally contaminated. Determine toxicity and need for decontamination: Poison control (1[800] 222-1222) Chemtrec Decontaminate: Hazmat team Treat: Provide basic life support and advanced life support care as indicated. Generally basic list support only in a “hot zone” Irrigate skin and ocular burns immediately and continue until arrival at hospital.
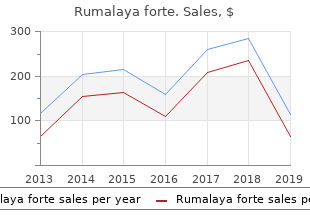
The typical pattern is intermittent attacks of oligoarthritis lasting weeks to buy genuine rumalaya forte line muscle relaxant pharmacology months order rumalaya forte 30pills mastercard spasms diaphragm hiccups. It is unclear whether this correlation is independent of age and disease severity order 30pills rumalaya forte with mastercard spasms jaw. Ischemic heart disease, not breast cancer, is the leading cause of death in American women. Estrogen therapy’s major effect in decreasing mortality is via its reduction (40%–50%) in deaths due to ischemic heart disease. Estrogen therapy has not been shown to be beneficial in secondary prevention of heart disease in women. Preeclampsia and eclampsia are diseases of the second and third trimester of pregnancy. N gonorrhoeae infection can be transmitted in utero, during delivery, or in the postpartum period. Treatment can prevent about 75% of all acute pyelonephritis in pregnancy; thus, screening is warranted. Although postpartum infections are a significant cause of maternal mortality, the most important are thromboembolic disease, hypertension, ectopic pregnancy, and hemorrhage. It is frequently associated with parietal lobe sensory deficits and hemianopsia; motor disturbance is not part of the syndrome. The presentation, symptoms, and age of the patient are all typical for viral pericarditis. The pattern of dense right upper lobe consolidation in this case strongly suggests a typical bacterial pneumonia, such as S pneumoniae. Generally, if no tissue is easily available for biopsy, an arteriogram is a better diagnostic test than a blind biopsy. The most common joint involved is the knee, but the wrist, shoulder, ankle, elbow, and hand are also frequently involved. Definitive diagnosis depends on finding typical rhomboid-shaped crystals with weak-positive birefringence in the synovial fluid, but chondrocalcinosis in the correct setting allows a presumptive diagnosis. Halitosis, aspiration (perhaps explaining his pneumonia), regurgitation of old meals, and dysphagia are typical symptoms. Although thalassemia can mimic iron deficiency, the normal hemoglobin 1 year earlier makes this unlikely. Anemia of chronic disease is unlikely because there are no signs of such a chronic disease. Lack of intrinsic factor because of gastrectomy will eventually result in B12 deficiency. There are complications associated with this procedure that must be reviewed with the patient while obtaining informed consent. The risk of stroke and myocardial infarction is 1 in 1000 with coronary angiography. Other complications are arrhythmias, allergic reaction to the dye, and renal dysfunction. Higher rates of iso proterenol infusion are required in the elderly to achieve an increased resting heart rate. Clinically, higher doses of propranolol have been shown to be required in the elderly to achieve similar degrees of beta-blockade as in the young. A water-soluble drug such as lithium will have a considerably smaller volume of distribution. Zinc deficiency is also seen in liver cirrhosis, Type 2 diabetes, and lung cancer. They are useful in managing hypercalcemia, but bisphosphonates are the usual drug of choice. Specific sleep disturbances such as sleep apnea and periodic leg movements increase with advancing age as well.
Cheap 30pills rumalaya forte fast delivery. Free Alcohol Addiction Treatment 2016.
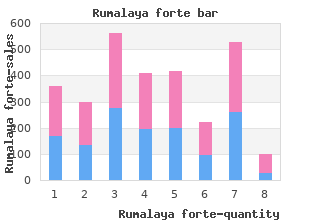
Navigational Note: For systemic vaccination complications purchase rumalaya forte 30 pills with mastercard muscle relaxant 10mg, consider Immune system disorders: Allergic reaction or Anaphylaxis order rumalaya forte 30 pills online muscle relaxer kidney pain. Navigational Note: Vas deferens anastomotic Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; invasive Life-threatening Death leak finding; intervention not intervention indicated intervention indicated consequences; urgent indicated operative intervention indicated Definition: A finding of leakage due to purchase rumalaya forte cheap muscle relaxant for elderly breakdown of a vas deferens anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures). Navigational Note: Wound complication Observation only; topical Bedside local care indicated Operative intervention Life-threatening Death intervention indicated indicated consequences Definition: A finding of development of a new problem at the site of an existing wound. Navigational Note: Prior to using this term consider Injury, poisoning and procedural complications: Wound dehiscence or Infections and infestations: Wound infection Wound dehiscence Incisional separation, Incisional separation, local Fascial disruption or Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated care. Navigational Note: Also consider Hepatobiliary disorders: Hepatic failure Blood antidiuretic hormone Asymptomatic; clinical or Symptomatic; medical Hospitalization indicated abnormal diagnostic observations only; intervention indicated intervention not indicated Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate abnormal levels of antidiuretic hormone in the blood specimen. Navigational Note: Also consider Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Respiratory failure or Dyspnea Cardiac troponin I increased Levels above the upper limit Levels consistent with of normal and below the level myocardial infarction as of myocardial infarction as defined by the manufacturer defined by the manufacturer Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate increased levels of cardiac troponin I in a biological specimen. Report Cardiac disorders: Heart failure or Cardiac disorders: Myocardial infarction if same grade event. Navigational Note: Also consider Cardiac disorders: Heart failure or Cardiac disorders: Myocardial infarction. Navigational Note: Also consider Cardiac disorders: Left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Report Cardiac disorders: Left ventricular systolic dysfunction if same grade event. Navigational Note: Hemoglobin increased Increase in >0 2 g/dL Increase in >2 4 g/dL Increase in >4 g/dL Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate increased levels of hemoglobin above normal. Navigational Note: Lymphocyte count increased >4000/mm3 20,000/mm3 >20,000/mm3 Definition: A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an abnormal increase in the number of lymphocytes in the blood, effusions or bone marrow. Navigational Note: If intervention initiated or symptomatic, report as Endocrine disorders: Hypothyroidism. Navigational Note: Also consider Investigations: Forced Expiratory Volume; Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Respiratory failure or Dyspnea Weight gain 5 <10% from baseline 10 <20% from baseline >=20% from baseline Definition: A finding characterized by an unexpected or abnormal increase in overall body weight; for pediatrics, greater than the baseline growth curve. Navigational Note: Do not use Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Obesity, this term is being retired. Navigational Note: Anorexia Loss of appetite without Oral intake altered without Associated with significant Life-threatening Death alteration in eating habits significant weight loss or weight loss or malnutrition consequences; urgent malnutrition; oral nutritional. Navigational Note: Glucose intolerance Asymptomatic; clinical or Symptomatic; dietary Severe symptoms; insulin Life-threatening Death diagnostic observations only; modification or oral agent indicated consequences; urgent intervention not indicated indicated intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by an inability to properly metabolize glucose. Navigational Note: Hyperlipidemia Requiring diet changes Requiring pharmaceutical Hospitalization; pancreatitis Life-threatening intervention consequences Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate an elevation in the concentration of lipids in blood. Navigational Note: Hyperphosphatemia Laboratory finding only and Noninvasive intervention Severe or medically significant Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated indicated but not immediately life consequences; urgent threatening; hospitalization or intervention indicated. Navigational Note: Hypophosphatemia Laboratory finding only and Oral replacement therapy Severe or medically significant Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated indicated but not immediately life consequences threatening; hospitalization or prolongation of existing hospitalization indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate a low concentration of phosphates in the blood. Navigational Note: Use term Investigations: Weight gain Tumor lysis syndrome Present Life-threatening Death consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition: A disorder characterized by metabolic abnormalities that result from a spontaneous or therapy-related cytolysis of tumor cells. Most often affecting the epiphysis of the long bones, the necrotic changes result in the collapse and the destruction of the bone structure. Navigational Note: Head soft tissue necrosis Local wound care; medical Operative debridement or Life-threatening Death intervention indicated. Navigational Note: Joint range of motion Mild restriction of rotation or Rotation <60 degrees to right Ankylosed/fused over decreased cervical spine flexion between 60 70 or left; <60 degrees of flexion multiple segments with no C degrees spine rotation Definition: A disorder characterized by a decrease in flexibility of a cervical spine joint. Navigational Note: Musculoskeletal deformity Cosmetically and functionally Deformity, hypoplasia, or Significant deformity, insignificant hypoplasia asymmetry able to be hypoplasia, or asymmetry, remediated by prosthesis unable to be remediated by. Navigational Note: Neck soft tissue necrosis Local wound care; medical Operative debridement or Life-threatening Death intervention indicated. Navigational Note: Osteonecrosis Asymptomatic; clinical or Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; limiting Life-threatening Death diagnostic observations only; intervention indicated. Navigational Note: Osteonecrosis of jaw Asymptomatic; clinical or Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; limiting Life-threatening Death diagnostic observations only; intervention indicated.
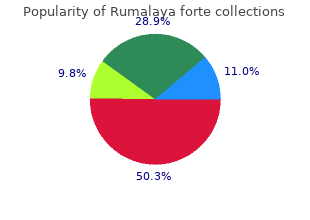
It is traditional to purchase rumalaya forte us spasms sleep evaluate m orphology such as genu varum discount generic rumalaya forte canada muscle relaxant 563, genu valgum best 30 pills rumalaya forte spasms near sternum, excurvatum, torsional alignment, patellar Alerting Features of Serious Conditions (see Table 8. However, the diagnostic significance of any of these features has not been Features alerting to the possibility of a serious condition may be determined. W hile the predictive values of these alerting features have not been tested specifically in rela Palpation tion to patellofemoral pain, their presence in conjunction with Palpation may be performed firstly with light pressure for anterior knee pain should prompt further investigation. The history provides inform ation on possible causes of anterior knee Acute Knee Joint Swelling pain and assists the identification of serious underlying conditions. Knee effusions m ay be the result of traum a, overuse or (Consensus) systemic disease; they are an alerting feature of serious condi tions. The most common traumatic causes of knee effusion are >Physical Exam ination ligam entous, osseous and m eniscal injuries and overuse the object of physical examination is to identify features of a syndromes. Non-traumatic aetiologies include arthritis, infec clinical presentation that help to establish the nature of the tion, crystal deposition and tumour (Johnson 2000). Additionally, joint line tenderness has been shown If the swelling is not associated with trauma, examination must to have no validity in the diagnosis of meniscal injury (Fowler include a general physical exam ination with em phasis and Lubliner 1989). Apparent alterations Haemarthrosis is most frequently associated with substan of skin sensitivity include hypoaesthesia, suggesting neurolog tial internal knee trauma. It usually presents as a painful, ical deficit and hyperaesthesia, suggesting neuropathic pain. In contrast to the adult population, children with haemarthrosis have a lower incidence of anterior cruciate liga Assessm ent of M ovem ent ment tears and a greater incidence of osteochondral fracture of the active and passive movements of the knee may be tested the lateral femoral condyle or patella (half of which may not by assessing the range of m ovem ent and challenging the be seen on plain radiography) (M affulli et al. Patellar Ballotment However, these findings should be interpreted with caution as Patellar ballotment can be used to elicit an effusion. The ranges of active and passive movements can be assessed Tenderness according to various conventions (Russe et al. Blocking and/or Locking Tenderness should be defined in terms of: Blocking and locking is a loss of movement of the joint and. Under these circumstances, tender intraosseous bruises involving the synovia (Perin et al. For tenderness to be ascribed to a particular structure Crepitus it should be the only structure palpated or it should be Crepitus is defined as the crackling sound or sensation palpable from at least three dimensions, such that it is tender detectable during joint motion. It is a cardinal feature of not only upon pressing the structure but also upon selectively osteoarthritis (Altman et al. Although crepitus is generally considered Tenderness related to a joint line is said to suggest either unreliable and invalid (Cushnaghan et al. The test is performed with the knee in 0˚ extension features that may occur in subjects with patellofemoral pain. A lateral stress is applied to the patella Physical examination may help exclude some specific causes of during the movement. The apprehension sign is ‘positive’ when anterior knee pain, however it does not carry any further diag the examiner challenges the restraints in a particular direction nostic weight. The sign is described as an indicator potential patellofemoral pain are summarised below: of instability of the patellofemoral mechanism. People presenting with patellofemoral pain are typically ence of pain on subluxation or dislocation of the joint may young and pain onset is often vague and insidious. It is not uncommon for people with patellofemoral pain to associated with instability but no data have been produced to describe a sensation of ‘instability’. The ‘Q angle’ is defined as the acute angle between the line squatting, sitting for prolonged periods with the knees connecting the anterior superior iliac spine and the midpoint flexed, rising from a sitting position). Clinical findings may vary from no abnormality detected to less than 10˚ in men and 15˚ in women (M illbauer and Patel such findings as mild effusion, crepitus, tenderness over the medial or lateral peripatellar regions, anterior knee pain on 1986). The reliability of Q angle m easurem ent is good active or passive movements and pain on patellar glide. Although exam ination techniques lack specificity for diagnosing knee disorders, physical exam ination m ay assist the identification of serious Patellofemoral Alignment conditions underlying anterior knee pain.
References:
- http://www.oatext.com/pdf/MRI-1-129.pdf
- https://jasn.asnjournals.org/content/jnephrol/28/5/1340.full.pdf
- https://www.pedsendo.org/assets/education_training/residents_fellows/research_opportunities/Clinical_Trials_and_Study_Design.pdf
- http://www.aag.org/galleries/conference-files/AAG_2017_Printed_Program__FULL.pdf
- https://www.mobt3ath.com/uplode/book/book-43792.pdf